The way we shop, seek entertainment and live is undergoing rapid change. Consumer lifestyles are more diverse than ever – there is no longer one size fits all approach.
When deciding to bring a new product to the market it can be very complex, knowing that around 95% of most new products aren’t successful within the first year its vital that your New Product Development (NPD) process is the best it can be. Despite the extensive research on how to achieve success in NPD, firms continue to deliver products that fail and therefore NPD ranks among the riskiest and most confusing tasks for most companies.
In order to influence consumer behaviour, we first have to understand what drives it. The problem is: most consumers don’t know why they do what they do. Their behaviours are automatic habits driven by need-states that even the consumer is often unaware of, for example, think about when you pick a packet of chewing gum up off the shelf. Do you stand and question which pack you’re going to purchase or do you find yourself holding the same pack you always do? People may well like a new product, may even try it – but for long-term success we need them to change their habits.
Therefore, it is essential to understand potential consumers, the market, and competitors within the same industry in order to develop products that consumers will purchase and ultimately value.
Many researchers have tried to develop a model that captures the relevant stages of the NPD process over the years. The Booz, Allen and Hamilton (1982) model, also known as the BAH model, it incorporates all of the stages involved in bringing a product from concept or idea through to market release and is still widely in use today.
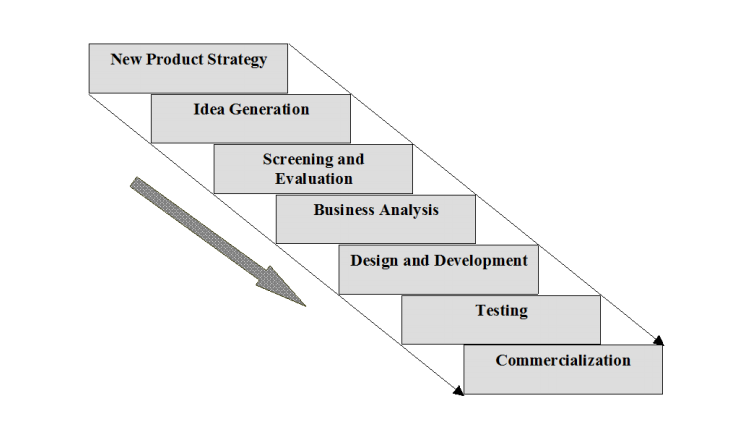
Stage 1: New Product Strategy
Companies must initially set objectives and create a clear strategy to meet them when beginning an NPD project. This is to provide guidance throughout the whole process. The objectives are to provide an understanding of what should be achieved by the product/services and what is expected of the team, which in time will change due to the influence of the market.
Stage 2: Idea Generation
The idea generation is where the search for product/service ideas begins – this must correspond with the objectives set during the New Product Strategy stage. The main focus of this stage is to produce a selection of different ideas – in the study conducted by Booz, Allen and Hamilton (1982), it was stated that a company has to generate at least seven ideas for one to be worthwhile. Throughout this stage, ideas can be generated through a range of different methods, such as, internal sources (i.e. research team), external sources (i.e. competitors), or from outsourcing market research to uncover what the consumer really wants – this is usually the most successful route. Emotional Logic's behavioural insight can help you shorten this process by quickly understanding usage habits and underlying needs.
Stage 3: Screening and Evaluation
The screening and evaluation stage are to determine which ideas should go on for further investigation – although the new product ideas pool decreases, the chance of success overall in the market increases.
Each idea should be projected as a product in the market where it can be evaluated against the competition. Through screening and evaluation, it helps you get a deeper understanding of the product/service that delivers the most value to the company. Making a solid choice can determine the overall success of the business. Emotional Logic offers an implicit testing programme that helps you to quickly screen large sets of ideas to find those with most potential.
Stage 4: Business Analysis
This stage prevents a company from spending mass amounts of money – it clearly defines the product/service and confirms if it is worthwhile to move forward with the process. This can be determined through a hypothetical business plan to identify product features, potential barriers against competition, market share and potential sales summary. These must be predicted in order to be deemed successful and move forward onto the next stage. Using a set format such as Emotional Logic's sales projector is a fast way to complete this stage.
Stage 5: Design and Development
During Design and Development, the ideas that are successful get created into actual products. The team who are working on the project can begin to create prototype and test marketing campaigns. This stage is to build the product/service to meet customer requirements – but this all has to be done within budget and to the required specifications.
However, the Design and Development stage can cause many implications, for example, when on-paper ideas are translated into real-life products – it is never as easy as it is thought to be.
Stage 6: Testing
Testing is used to provide final and overall verification of the entire project – this is your chance to discover if it will work within the chosen market. The information that is gathered from the testing stage is used to further develop the product. It is essential that this stage is carried out appropriately to prevent failure at the real product launch. Different testing and research can be completed at this stage: focus groups, prototype testing and test marketing. It is critical that this stage goes beyond consumers simply stating whether they like the product - as self-reported intention to buy is a poor predictor of future sales. Emotional Logic use implicit techniques to get closer to true consumer reactions at this stage.
Once feedback has been generated through testing it gives the company another chance to ready their products for entry into the marketplace. Please be aware that testing should be happening throughout the whole NPD process, and not limited to just this stage.
Stage 7: Commercialization
Finally, your product is ready to be released into the world. At this stage, customer feedback should be collected actively to ensure the product is meeting needs and expectations of the customer. If there are any changes to be made, now is the time to do it.
How we can help:
During each stage Emotional Logic have the tools to help stimulate behavioural change to reduce the complexity of your NPD process, for example:
An FMCG brand was looking to increase their market share and grow the category they were operating in by activating new consumption situations. Emotional Logic was asked to screen, then test and refine a number of new product ideas for their potential to change consumer behaviour and activate growth for both the brand and the category.
We helped discover new insights:
Like many FMCG purchases this category was very habit driven with consumers reaching for 2-3 brands without really taking notice of new options. Our Motivation Deep Dive revealed what held existing behaviours in place and how to unhook those habits. We tested product concepts for appeal and ability to attract attention at point of purchase. This enabled the brand to develop a strong new product concept that will disrupt the category and create new consumption occasions.
Developing a new product or service involves committing significant time and resources to a project that may or may not ultimately be successful. The right approach helps to reduce that risk – Emotional Logic unhook a clearer picture of who your core customers are and how to reach them simply and effectively. Get in touch today.
